1 国防科技大学理学院, 湖南 长沙 410073
2 国防科技大学量子信息学科交叉中心, 湖南 长沙 410073
3 北京邮电大学电子工程学院, 北京 100876
光学成像是人们获取信息最重要的技术手段之一。关联成像作为一种基于光场高阶关联发展起来的新技术, 利用单个点探测器就可以实现对面目标的成像, 具有物像分离、探测灵敏度高、抗干扰能力强等优点, 为光学成像技术的发展带来了新的机遇。但关联成像以时间换空间的多帧累积成像模式, 严重限制了图像的获取效率。为了解决该问题, 除了进行系统结构、光源和探测方法优化设计外, 研究高效的图像重构算法也是提高成像质量和成像速度最有效的方法之一。好的图像重构算法不仅能大大降低成像所需的测量次数, 提高信息提取效率和重构图像质量, 还能降低对成像系统硬件的要求, 是关联成像技术走向实用的关键。近年来, 关联成像图像重构算法不断演变, 发展出很多不同类型的重构算法。本文简要回顾了关联成像的原理机制, 进而在此基础上系统介绍了几种主要关联成像算法的基本原理, 并分析了其优缺点和适用场景。
量子光学 关联成像 强度关联 伪逆算法 深度学习 quantum optics ghost imaging intensity correlation pseudo-inverse algorithm deep-learning
1 国防科技大学 文理学院,湖南 长沙 410073
2 国防科技大学 量子信息学科交叉中心,湖南 长沙 410073
光学成像因其分辨率高,信息量丰富,具有其他探测和感知技术不可替代的地位,是人们获取信息最重要的技术手段之一。光子是光学成像系统中的信息载体。光学图像的高质量重构,依赖于对信号光子的高效耦合和对光信息的精准解耦。然而,在遥感或生物成像等重要应用场景中,由于作用距离远或辐照功率低,到达探测面的物体信号光子数少,信噪比低,对光学系统设计、信号探测和图像恢复都带来了极大困难,严重限制了光学成像性能。如何在极弱光条件下获得高质量图像,是光电成像系统研究的基础性难题,也是推动光学成像不断向更大视场、更远作用距离、更高信息通量发展亟待克服的关键技术。近年来,在光场调控和量子探测技术支撑下,并基于光场的高阶经典/量子关联发展起来的关联成像,由于探测灵敏度高、抗干扰能力强,为发展极弱光条件下的光学成像技术带来了新的机遇。文中将简要回顾关联成像的原理机制,在此基础上系统介绍极弱光条件下关联成像方案和方法。并尝试从光子动力学层面解释这些方法的物理本质,讨论这些方法的能力极限,比较这些方法所适用的场景。
成像系统 关联成像 弱光成像 光子计数 单光子成像 imaging system ghost imaging weak light imaging photon counting single photon imaging 红外与激光工程
2021, 50(12): 20210819
1 国防科技大学文理学院物理系, 湖南 长沙 410073
2 国防科技大学量子信息学科交叉中心, 湖南 长沙 410073
关联成像是一种基于光场高阶关联获取物体信息的新型主动成像机制,具有高灵敏、抗干扰等特点,在生物医学、遥感成像等领域有广阔的应用前景。关联成像需要多次采样来重构物体图像,成像过程需要一定的时间,在此期间物体和成像系统的相对运动会导致图像质量退化。如何提升对运动物体的成像能力是关联成像走向应用需要解决的关键问题之一。简要回顾了关联成像的基本概念,详细介绍了运动物体关联成像的原理方法、发展历程及研究现状,比较了所述技术所适用的场景并展望了其发展趋势。
激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(10): 1011001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, College of Liberal Arts and Science, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 Interdisciplinary Center of Quantum Information, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
Applications of ghost imaging are limited by the requirement on a large number of samplings. Based on the observation that the edge area contains more information thus requiring a larger number of samplings, we propose a feedback ghost imaging strategy to reduce the number of required samplings. The field of view is gradually concentrated onto the edge area, with the size of illumination speckles getting smaller. Experimentally, images of high quality and resolution are successfully reconstructed with much fewer samplings and linear algorithm.
computational ghost imaging adaptive imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(4): 041102
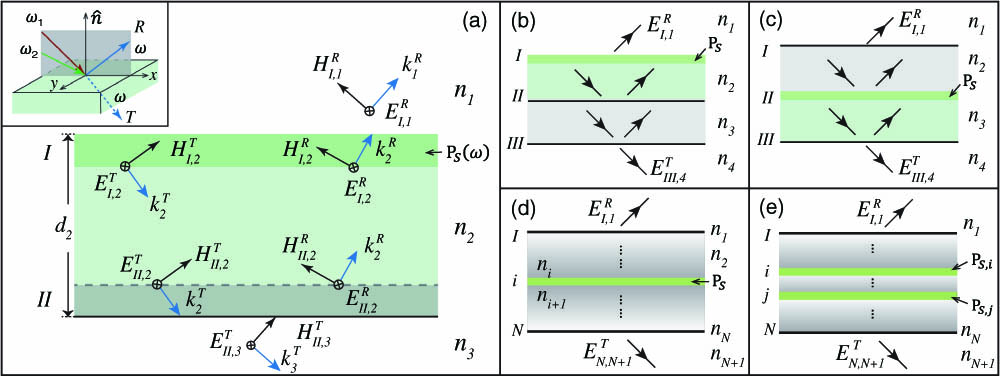
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Physics Department, State Key Laboratory of Surface Physics, Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Photonic Structures (MOE), Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures (Nanjing), Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
In optical studies on layered structures, quantitative analysis of radiating interfaces is often challenging due to multiple interferences. We present here a general and analytical method for computing the radiation from two-dimensional polarization sheets in multilayer structures of arbitrary compositions. It is based on the standard characteristic matrix formalism of thin films, and incorporates boundary conditions of interfacial polarization sheets. We use the method to evaluate the second harmonic generation from a nonlinear thin film, and the sum-frequency generation from a water/oxide interface, showing that the signal of interest can be strongly enhanced with optimal structural parameters.
190.4400 Nonlinear optics, materials 260.3160 Interference 310.4165 Multilayer design Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(8): 081901
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Science, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 Interdisciplinary Center of Quantum Information, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
Correlation imaging is attracting more and more attention as a novel imaging technique taking advantage of the high-order coherence of light fields. To reconstruct an image of the object, many frames of different speckle patterns are required. Therefore, the speed of imaging is strongly limited by the speed of the refreshing rate of the light field. We propose a coprime-frequencied sinusoidal modulation method for speckle pattern creation using a spatial light modulator in a computational ghost imaging system to increase the speed of imaging. The performance of the proposed method is discussed as well.
110.6150 Speckle imaging 030.6600 Statistical optics 110.2945 Illumination design Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(11): 111103





